1 中国工程物理研究院 应用电子学研究所,四川 绵阳,621900
2 中国工程物理研究院研究生院,四川 绵阳,621900
3 中国工程物理研究院 流体物理研究所,四川 绵阳,621900
4 95972部队,甘肃 酒泉,735300
在探测目标尺寸小且距离远时,由于光电系统的视场角很小,有效的目标前级引导是光电系统跟瞄目标的前提。目标引导的本质是将大地坐标系下的目标点转换至光电系统局部坐标系下,转换过程中引入一系列旋转和平移参数,其准确程度决定了最终的目标引导精度。提出基于无人机航迹的光电系统引导误差校正方法,通过围绕光电系统周围无人机航迹数据,求解引导数据计算过程中坐标变换的最优参数,进而提高目标引导精度。在本项目搭建的实验装置上实现了方位引导标准方差小于0.052°,俯仰引导标准方差小于0.04°,最大误差不超过0.7°。目标前级引导的引导精度越高,光电系统捕获目标速度越快,对于提高目标处置相应速度具有重要意义。
目标引导 引导误差 目标探测 target guidance guidance error target detection
空军工程大学航空等离子体动力学重点实验室,陕西 西安 710038
利用光电二极管采集熔池辐射信息,深入挖掘熔池辐射信号中的工艺及过程稳定性信息。基于统计学分析方法研究了不同层高、不同基板位置、不同扫描线角度等过程因素对熔池辐射信号的影响,分析了熔池辐射信息与热积累、烟尘遮蔽等物理现象之间的内在联系,建立了“信号-过程因素-物理机制”之间的对应关系。结果表明,熔池辐射强度均值随层高的增加有明显升高趋势;顺、逆风向的熔池辐射强度波形呈“左偏”、“右偏”形状特征;不同位置的熔池辐射强度差异明显;扫描线角度是否沿着样件摆放方向明显影响强度均值。其典型规律表明这些特征可以作为质量监控的重要参考。
激光技术 激光粉末床熔融 光电二极管 过程因素 熔池辐射强度 中国激光
2022, 49(14): 1402206

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Nanjing University, National Laboratory of Solid-state Microstructures, School of Physics, Research Institute of Superconducting Electronics, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing, China
2 Sun Yat-sen University, State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Electronics and Information Technology, Guangzhou, China
Integrated photonics provides a route to both miniaturization of quantum key distribution (QKD) devices and enhancing their performance. A key element for achieving discrete-variable QKD is a single-photon detector. It is highly desirable to integrate detectors onto a photonic chip to enable the realization of practical and scalable quantum networks. We realize a heterogeneously integrated, superconducting silicon-photonic chip. Harnessing the unique high-speed feature of our optical waveguide-integrated superconducting detector, we perform the first optimal Bell-state measurement (BSM) of time-bin encoded qubits generated from two independent lasers. The optimal BSM enables an increased key rate of measurement-device-independent QKD (MDI-QKD), which is immune to all attacks against the detection system and hence provides the basis for a QKD network with untrusted relays. Together with the time-multiplexed technique, we have enhanced the sifted key rate by almost one order of magnitude. With a 125-MHz clock rate, we obtain a secure key rate of 6.166 kbps over 24.0 dB loss, which is comparable to the state-of-the-art MDI-QKD experimental results with a GHz clock rate. Combined with integrated QKD transmitters, a scalable, chip-based, and cost-effective QKD network should become realizable in the near future.
quantum key distribution hybrid photonics single-photon detector Bell-state measurement time-multiplexing Advanced Photonics
2021, 3(5): 055002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Laboratory of Solid-state Microstructures, School of Physics, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
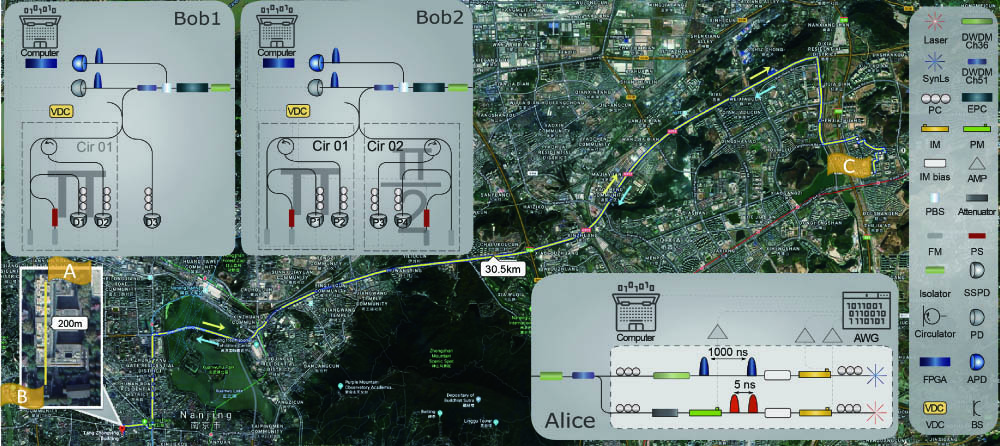
We employ quantum state and process tomography with time-bin qubits to benchmark a city-wide metropolitan quantum communication system. Over this network, we implement real-time feedback control systems for stabilizing the phase of the time-bin qubits and obtain a 99.3% quantum process fidelity to the ideal channel, indicating the high quality of the whole quantum communication system. This allows us to implement a field trial of high-performance quantum key distribution using coherent one way protocol with an average quantum bit error rate and visibility of 0.25% and 99.2% during 12 h over 61 km. Our results pave the way for the high-performance quantum network with metropolitan fibers.
quantum process tomography quantum networks quantum communication quantum key distribution Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(8): 082701
1 空军工程大学 等离子体动力学重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710038
2 中国人民解放军第五七一三工厂, 湖北 襄阳 441002
针对激光冲击强化涡轮机匣部件难以贴覆吸收保护涂层的问题, 提出无保护层激光冲击(LSPwC)+水砂纸磨除烧蚀层的复合工艺, 研究LSPwC对GH3044合金微观组织和力学性能的影响, 验证复合工艺的可行性。采用能谱仪(EDS)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和金相显微镜分析试样表层元素组成和微观组织, 通过测试残余应力和高周疲劳寿命表征其力学性能。结果表明, LSPwC在试样表层产生约10~15 μm的烧蚀层, 烧蚀层内碳、氧元素富集且残余拉、压应力交替存在, 烧蚀层以下晶粒和碳化物不同程度地均匀细化; 相比原始试样, LSPwC对GH3044合金疲劳寿命提升不明显; 水砂纸磨除烧蚀层后, 试样表面残余压应力约510 MPa, 影响深度层达1 mm, 疲劳寿命提高到原始试样的3倍。
激光冲击强化 GH3044合金 微观组织 残余应力 高周疲劳寿命 laser shock processing GH3044 alloy microstructure residual stress high cycle fatigue life 红外与激光工程
2018, 47(4): 0406005
空军工程大学 等离子体动力学重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710038
针对激光熔覆修复K403镍基高温合金构件组织粗大和力学性能下降的问题, 提出采用激光冲击强化技术对修复区进行表面强化。利用SEM观察不同区域微观组织, 利用显微硬度、残余应力和高温拉伸强度测试研究其力学性能。结果表明, 激光冲击强化细化试样表层晶粒; 强化后, 试样基体区和熔覆区表面硬度分别提高21%和8%, 影响深度约0.8 mm; 激光冲击在试样表层引入约610 MPa且均匀分布的残余压应力, 影响深度层达1.2 mm, 经保温处理后, 应力释放约18%, 但在表面仍残留较大的残余压应力; 激光冲击提高了材料高温拉伸强度约15%, 解决了激光熔覆修复K403镍基构件力学性能下降的问题。
激光冲击强化 K403合金 微观组织 残余应力 拉伸强度 laser shock processing K403 alloy microstructure residual stress tensile strength 红外与激光工程
2017, 46(9): 0906003





